elfcam
Fiber optic specialist
- All products
- Optical Cable
-
-
- Simplex to Simplex Optical Patch Cord
- SC/APC-SC/APC (Orange,SFR,Bouygues) White€5,87 incl. tax
- SC/APC-SC/APC (Orange,SFR,Bouygues) Yellow€6,36 incl. tax
- SC/APC-SC/UPC (Free) White€5,38 incl. tax
- SC/APC-SC/UPC (Free) Yellow€6,85 incl. tax
- LC/APC-LC/APC White
- LC/APC-LC/APC Yellow€8,81 incl. tax
- LC/APC-SC/APC White
- LC/APC-SC/APC Yellow€6,74 incl. tax
- LC/APC-LC/UPC White
- LC/UPC-SC/APC Yellow€7,34 incl. tax
- LC/UPC-SC/APC White
- LC/UPC-LC/UPC Yellow€5,99 incl. tax
- SC/UPC-SC/UPC White€6,66 incl. tax
- SC/UPC-SC/UPC Yellow
- E2000-LC/APC
- FC/PC-FC/APC7,83 € incl taxes
- FC/PC-FC/PC€8,81 incl. tax
- FC/PC-SC/APC€8,81 incl. tax
- SC/UPC-SC/UPC 5,0mm Black
- LC/APC-LC/APC 5,0mm Black
- Simplex to Simplex Optical Patch Cord
-
-
-
- Duplex Optical Patch Cord
- OM3 LC/UPC LC/UPC€8,81 incl. tax
- OM4 LC/UPC LC/UPC€8,81 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex LC/APC LC/APC€7,83 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex E2000/APC LC/APC
- OS2 Duplex LC/APC LC/UPC
- OS2 Duplex LC/UPC LC/UPC€8,81 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex SC/APC SC/APC8,81 € incl taxes
- OS2 Duplex SC/APC LC/UPC€8,62 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex SC/UPC LC/UPC€9,79 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex FC/PC FC/APC€9,79 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex FC/PC FC/PC€9,79 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex FC/PC SC/APC€9,79 incl. tax
- OS2 Duplex ST/UPC LC/UPC
- OS2 Duplex ST/UPC ST/UPC
- OM3 ST/UPC LC/UPC
- OM3 ST/UPC ST/UPC
- OM3 LC/UPC SC/UPC
- OM3 SC/UPC SC/UPC
- MPO 12Fibers39,81 € incl taxes
- MPO 8Fibers
- MPO 8Fibres Breakout
- Duplex Optical Patch Cord
-
-
-
- Outdoor Optical Cable
-
-
- Fiber Optic Cable with Armor
- Simplex SC/APC SC/APC in armored steel€10,99 incl. tax
- Simplex SC/APC SC/UPC in armored steel€12,69 incl. tax
- Simplex LC/APC SC/APC in armored steel
- Simplex LC/APC LC/APC in armored steel
- OS2 Duplex LC/UPC LC/UPC in armored steel
- OM3 Duplex LC/UPC LC/UPC in armored steel€39,99 incl. tax
- OM3 Duplex LC/UPC Armored Steel LC/UPC Black
- OM3 Duplex SC/UPC SC/UPC Black
- Fiber Optic Cable with Armor
-
- Fiber Optic Cable outside
- Fiber Optic Cable SC/APC - SC/APC (all operators)€56,99 incl. tax
- Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable 1-2-4 fibers
- Fiber Optic Cable (Indoor for work) 1-2-4 fibers
- OS2 Simplex SC/UPC-SC/UPC Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
- OS2 Duplex Fiber Optic Cable LC/UPC-LC/UPC Outdoor
- OS2 Simplex LC/APC LC/APC Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
- OM3 Duplex Fiber Optic Cable LC/UPC-LC/UPC Outdoor
- Fiber Optic Cable outside
-
-
- Optical Module
-
-
- Optical Module
- SFP SC Simplex TX1310
- SFP SC Simplex RX1310
- SFP SC Simplex Lot2 (TX1310-RX1310)
- SFP LC Simplex TX1310
- SFP LC Simplex RX1310
- SFP LC Simplex Lot2 (TX1310-RX1310)
- SFP LC Duplex Lot2 (OS2)
- SFP LC Duplex Lot2 (OM3/OM4)
- 10GSFP+ LC Duplex (OM3/OM4)
- 10GSFP+ LC Duplex (OM3/OM4) Lot 2
- 10GSFP+ LC Simplex 20km
- 10GSFP+ LC Duplex (OS2)
- 10GSFP+ LC Duplex (OS2) Batch 2
- SFP RJ45 (1,25G)
- 10GSFP+ RJ45
- 10G Direct Attach Cable (DAC)
- 25G Direct Attach Cable (DAC)
- 10G Direct Attached (AOC) Fiber
- 25G Direct Attached (AOC) Fiber
- Optical Module
-
-
-
-
-
- Optical Adaptation
-
-
- Adapter
- SC-SC APC Single Mode Adapter
- SC-SC UPC Single Mode Adapter
- LC/UPC-LC/UPC Single-mode duplex adapter
- LC/UPC-LC/UPC Multimode duplex adapter
- LC-LC APC Female-Female Single Mode Simplex Adapter
- LC-LC APC Single Mode Duplex Adapter
- LC-LC UPC Female-Female Single Mode Adapter
- SC-LC UPC Male-Female Single Mode Simplex Adapter
- SC-LC APC Male-Female Single Mode Simplex Adapter
- FC-LC UPC Male-Female Single Mode Adapter
- Simplex Single Mode FC-FC Adapter
- SC/APC-SC/APC Single Mode Duplex Adapter
- SC/APC-LC/APC Female-Female Single Mode Simplex Adapter
- SC/APC-LC/APC Female-Male Single Mode Simplex Adapter
- LC/UPC Optical Fiber Rapid Connector
- SC/APC Fiber Optic Rapid Connector
- Adapter
-
-
-
- pigtail
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 12 Fibers SC/APC Color
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 12 Fibers SC/UPC Color
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 12 Fibers LC/UPC Color
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 12 Fibers SC/APC White
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 12 Fibers SC/APC Yellow
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 12 Fibers LC/APC White
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 12 Fibers LC/APC Yellow
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 24 Fibers SC/APC White
- Fiber Optic Pigtail 48 Fibers SC/APC White
- Fiber Optic Pigtail (12 FO) OM3 LC/UPC
- Fiber Optic Pigtail (12 FO) OM4 LC/UPC
- pigtail
-
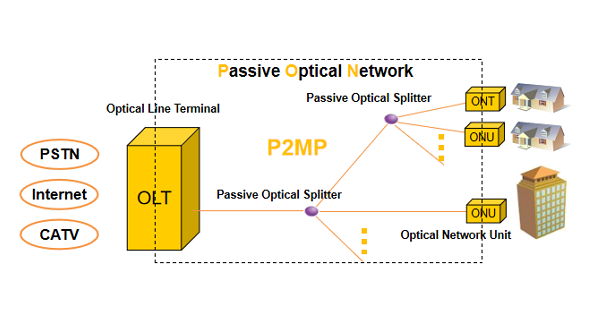
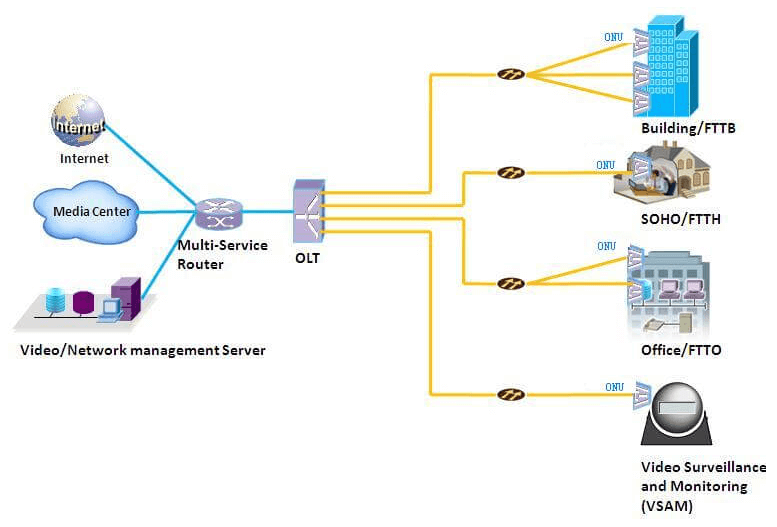
- Optical Network
- Optical Tool
-
-
- Tools
- ELFCAM K1 High Precision Cleaver
- ELFCAM SE High Precision Cleaver
- SE-09 Cleaver 48,000 Cuts
- Smoove Transparent for Optical Fiber Soldering€37,80 incl. tax / 1000 pieces
- Supvan LP5120M labeler
- Kevlar Scissors for Optical Fiber
- Kevlar Scissors for Optical Fiber Blue
- Fiber Optic Stripping Pliers
- Coaxial Coax Cable Stripping Pliers
- Kevlar Scissors for Optical Fiber + Ergonomic Stripping
- Tools
-
- Ethernet cable
- Optical Cable
- Solutions
- Information
- About us
Professional
elfcam
A4, 32 Avenue de l'épi d'or, 94800, Villejuif, France
Kolner Str.366, 40227 Dusseldorf, Deutschland